- Invasi Ukraina oleh Rusia
- Herba
- Sedatif
- Walter Sisulu
- Valerian (herb)
- Valerian
- Herbal tea
- Oneirogen
- List of San Francisco Bay Area wildflowers
- Lemon balm
- Tlalnepantla, Morelos
- Valeriana jatamansi
- Scutellaria galericulata
- Herbal medicine
- VALERIAN - Uses, Side Effects, and More - WebMD
- Valerian (herb) - Wikipedia
- Valerian: A safe and effective herbal sleep aid? - Mayo Clinic
- How Valerian Root Helps You Relax and Sleep Better - Healthline
- Valerian - Health Professional Fact Sheet - Office of Dietary ...
- Valerian Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
- Valerian Root Benefits, Uses, Dosage and Side Effects - Dr. Axe
- Valerian (Root): Uses, Benefits, Side-Effects - Holland & Barrett
- Valerian Root: 5 Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, and More - Health
- Valerian (Valeriana officinalis): Health Benefits, Ayurvedic Uses
valerian herb
Video: valerian herb
Valerian (herb) GudangMovies21 Rebahinxxi LK21
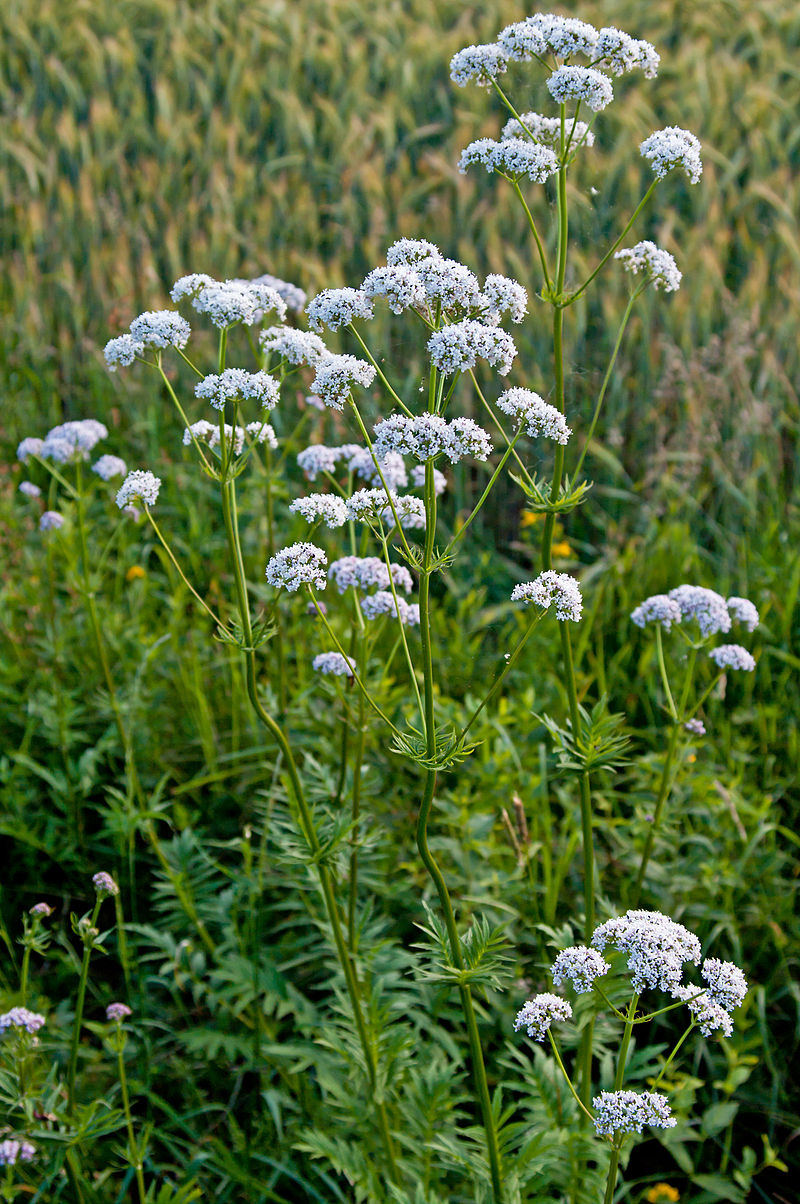
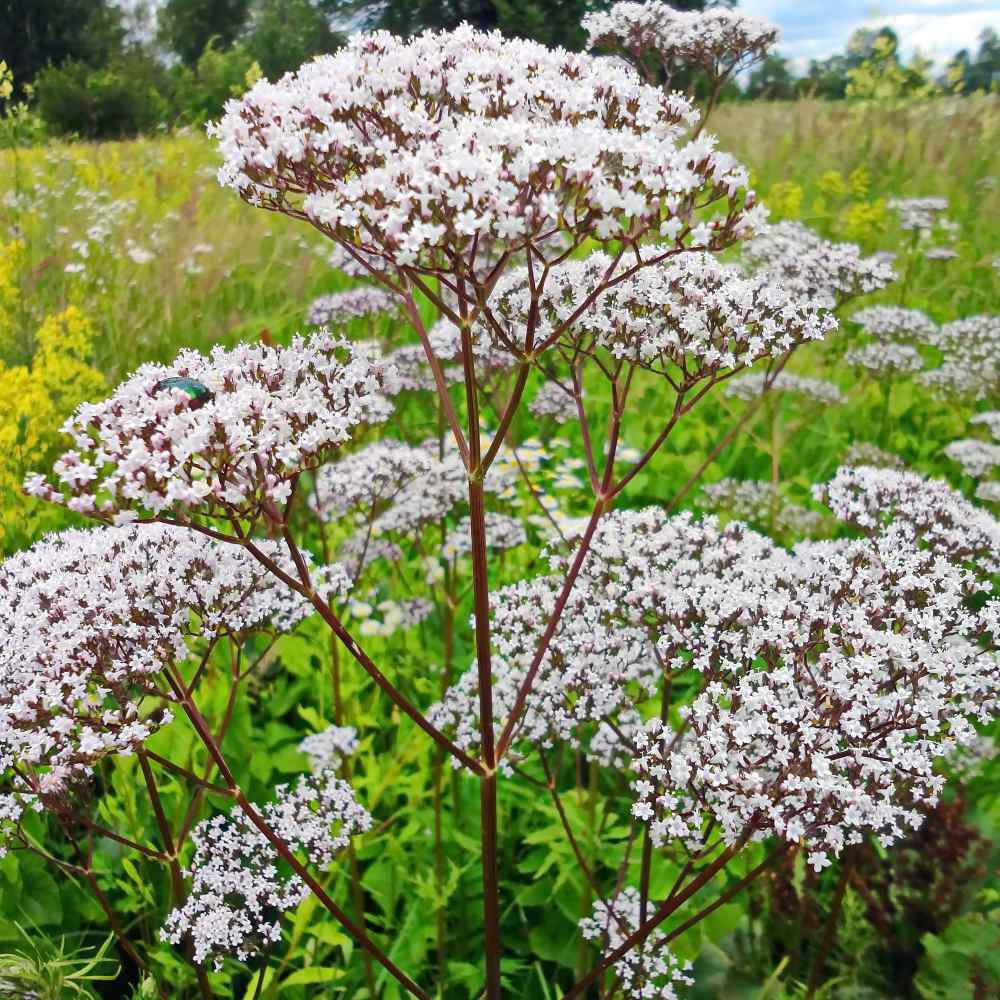
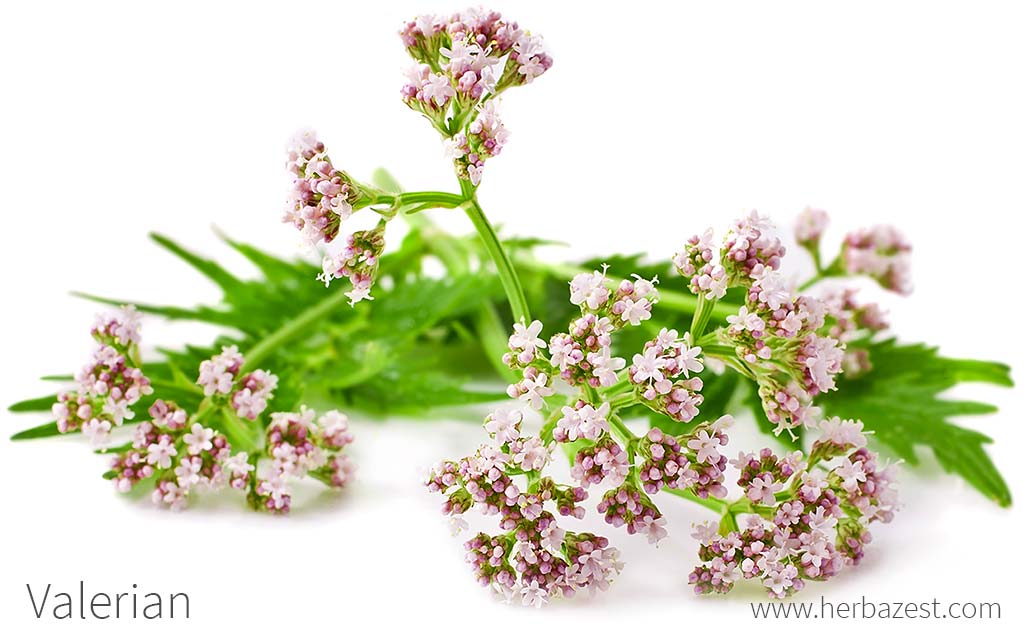
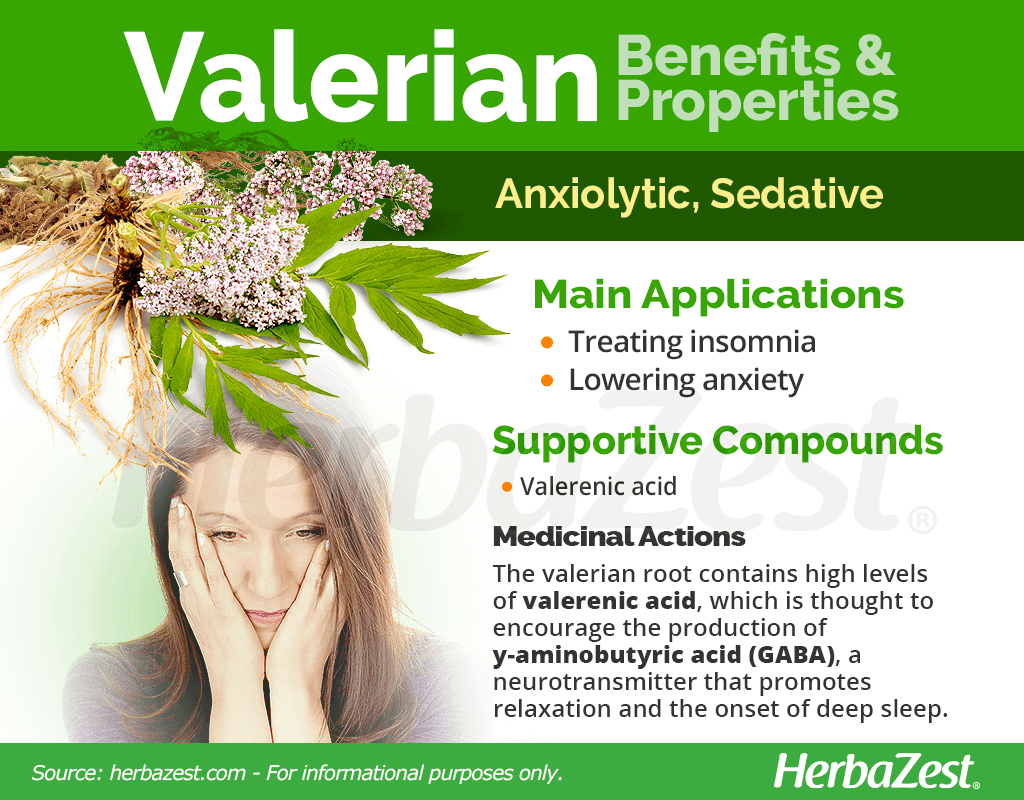
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis, Caprifoliaceae) is a perennial flowering plant native to Eurasia. It produces a catnip-like response in cats.
Crude extract of valerian root may have sedative and anxiolytic effects, and is commonly sold in dietary supplement capsules to promote sleep, but clinical evidence that it is effective for this purpose is weak or inconclusive.
Names
The name of the herb is derived from the personal name Valeria and the Latin verb valere (to be strong, healthy). Other names used for this plant include garden valerian (to distinguish it from other Valeriana species), garden heliotrope (although not related to Heliotropium), setwall and all-heal (which is also used for plants in the genus Stachys). Red valerian, often grown in gardens, is also sometimes referred to as "valerian", but is a different species (Centranthus ruber), from the same family but not very closely related. Valerian is also called cat's love for its catnip-like effects.
Description
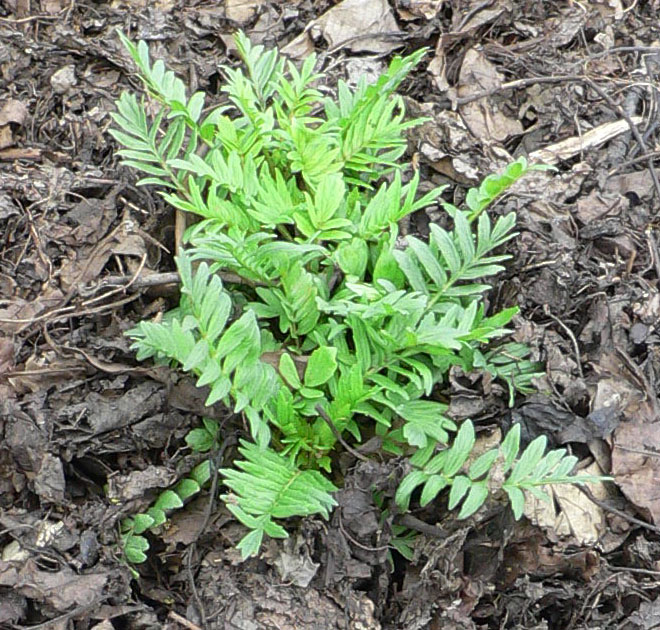
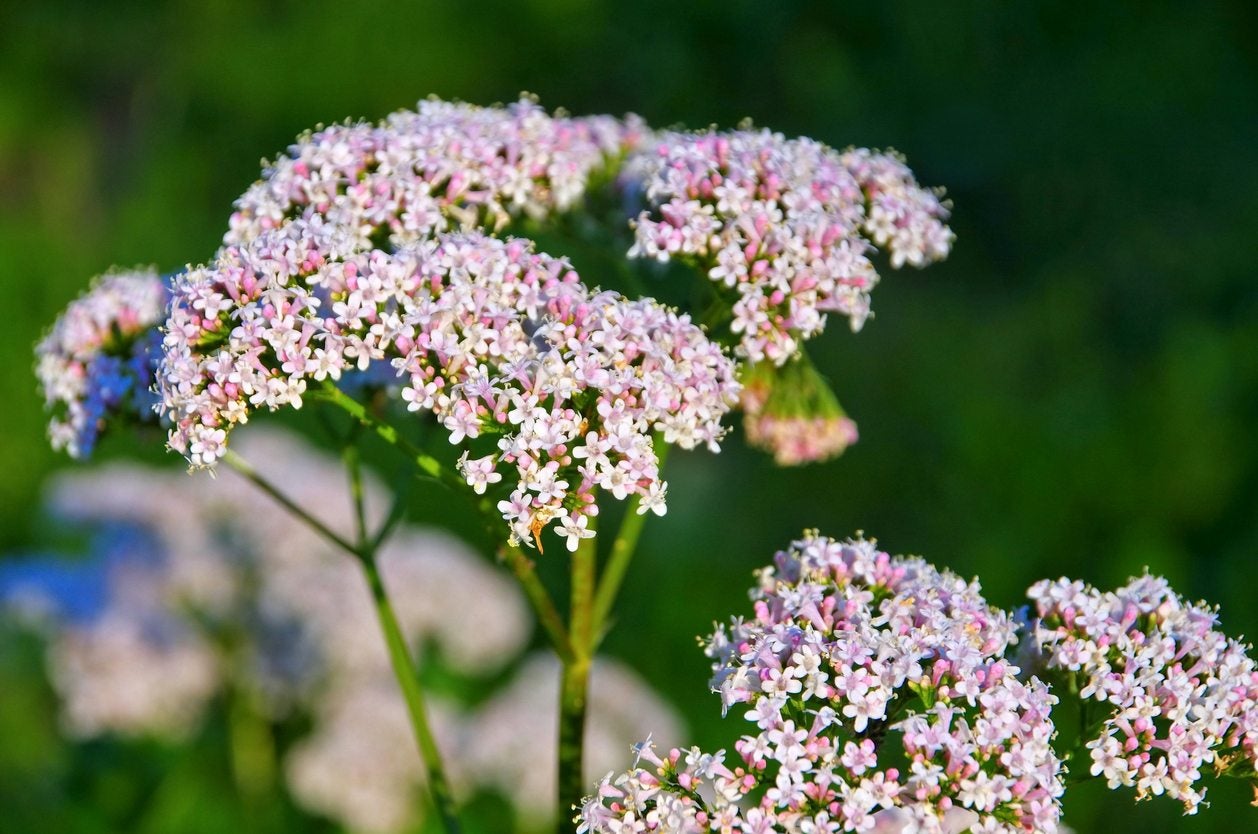
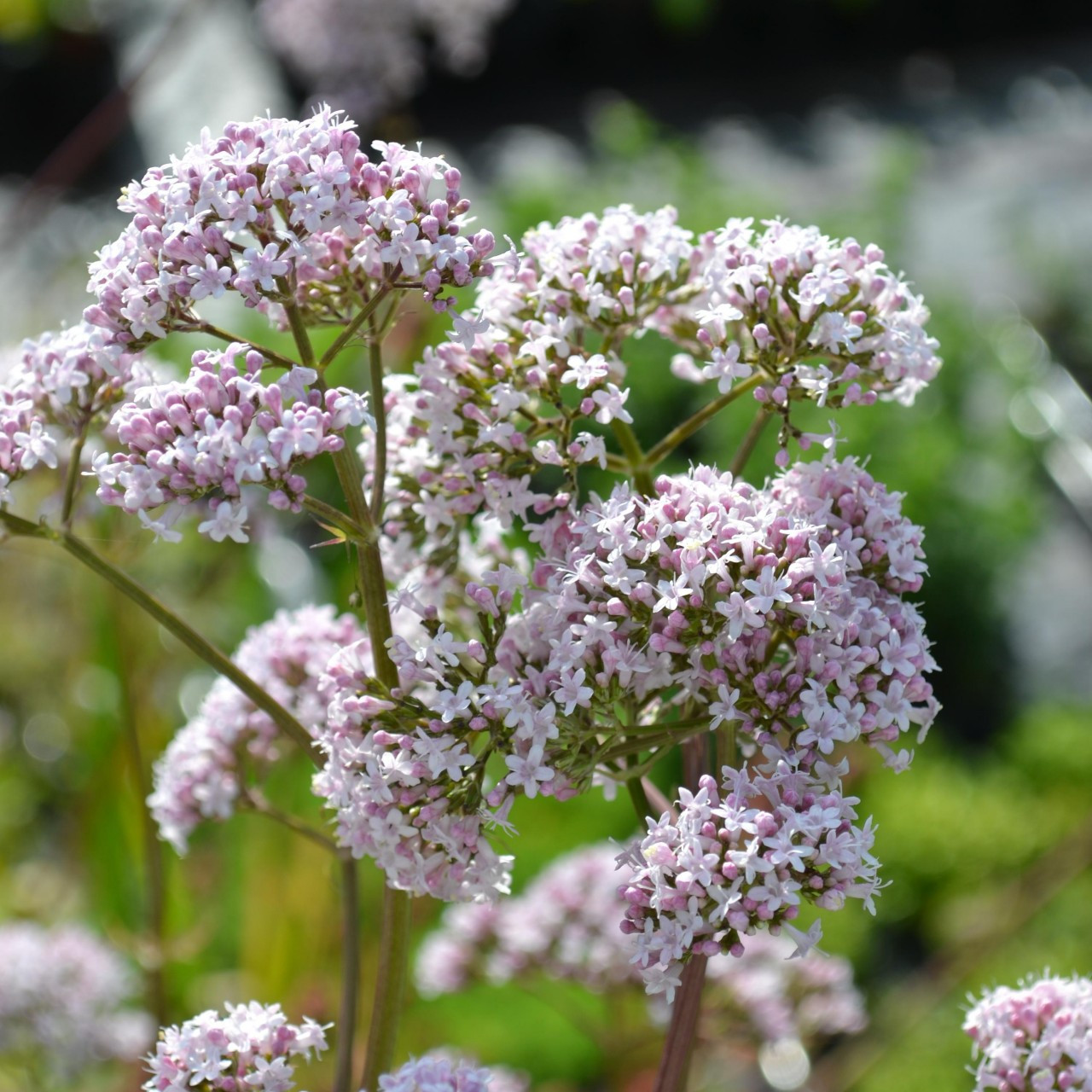
The plant grows up to 2 metres (7 feet) tall and 1 m wide. The erect stems are unbranched, with pinnately divided, toothed leaves. The flowers are light pink, grouped in both compound and secondary clusters.
In the summer the mature plant can bear sweetly scented pink or white flowers.
Distribution and habitat
The plant is native to Europe and Asia. It is widespread in Britain.
Ecology
The flowers attract many fly species, especially hoverflies of the genus Eristalis. The plant is consumed as food by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (butterfly and moth) species, including the grey pug.
= As an invasive species
=Valerian is considered an invasive species in many locations outside its natural range, including the U.S. state of Connecticut where it is officially banned, and in New Brunswick, Canada, where it is listed as a plant of concern.
= Effect on cats
=Valerian root is a cat attractant, containing attractant semiochemicals in a way similar to catnip, which can lead to a behaviour modification effect in cats. Its roots and leaves are one of three alternatives for the one-third of domesticated or medium-sized cats who do not feel the effects of catnip. Valerian root has also been reported to be attractive to rats and used to attract members of the family Canidae to traps.
Valerian extract
= Phytochemicals
=Known compounds detected in valerian include:
Alkaloids: actinidine, chatinine, shyanthine, valerianine, and valerine
Isovaleramide may be created in the extraction process.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Valeric acid
Isovaleric acid
Iridoids, including valepotriates: isovaltrate and valtrate
Sesquiterpenes (contained in the volatile oil): valerenic acid, hydroxyvalerenic acid and acetoxyvalerenic acid
Flavanones: hesperidin, 6-methylapigenin, and linarin
= Preparation
=The chief constituent of valerian is a yellowish-green to brownish-yellow oil present in the dried root, varying in content from 0.5 to 2.0%. This variation in quantity may be determined by location; a dry, stony soil yields a root richer in oil than moist, fertile soil.
= Traditional medicine
=Although valerian is a common traditional medicine used for treating insomnia, there is no good evidence it is effective for this purpose. Valerian has not been shown to be helpful in treating restless leg syndrome or anxiety.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved the health claim that valerian can be used as a traditional herb to relieve mild nervous tension and to aid sleep; the EMA stated that although there is insufficient evidence from clinical studies, its effectiveness as a dried extract is considered plausible.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine's 2017 clinical practice guidelines recommended against the use of valerian in the treatment of insomnia due to poor effectiveness and low quality of evidence.
Oral forms
Oral forms are available in both standardized and unstandardized forms. Standardized products may be preferable considering the wide variation of the chemicals in the dried root, as noted above. When standardized, it is done so as a percentage of valerenic acid or valeric acid. For commonly used doses, valerian is generally recognized as safe in the U.S.
Adverse effects
Because the compounds in valerian produce central nervous system depression, they should not be used with other depressants, such as ethanol (drinking alcohol), benzodiazepines, barbiturates, opiates, kava, or antihistamine drugs.
As an unregulated product, the concentration, contents, and potential contaminants in valerian preparations cannot be easily determined. Because of this uncertainty and the potential for toxicity in the fetus and hepatotoxicity in the mother, valerian use is discouraged during pregnancy. Headache and diarrhea have occurred among subjects using valerian in clinical studies.
Other uses
The young leaves can be cooked and the roots can be infused in hot beverages like hot chocolate.
In culture
Valerian has been used as a herb in traditional medicine since at least the times of ancient Greece and Rome. Hippocrates described its properties, and Galen later prescribed it as a remedy for insomnia. In medieval Sweden, it was sometimes placed in the wedding clothes of a bridegroom to ward off the "envy" of the elves. In the 16th century, Pilgram Marpeck prescribed valerian tea for a sick woman.
John Gerard's Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes, first published in 1597, states that his contemporaries found valerian "excellent for those burdened and for such as be troubled with croup and other like convulsions, and also for those that are bruised with falls". He says that the dried root was valued as a medicine by the poor in the north of England and the south of Scotland, such that "no brothes, pottages or phisicalle meates are woorth [worth] anything if Setwall [valerian] were not at one end".
The 17th-century astrological botanist Nicholas Culpeper thought the plant was "under the influence of Mercury, and therefore hath a warming faculty". He recommended both herb and root, and said that "the root boiled with liquorice, raisons and aniseed is good for those troubled with cough. Also, it is of special value against the plague, the decoction thereof being drunk and the root smelled. The green herb being bruised and applied to the head taketh away pain and pricking thereof."
Gallery
See also
Orvietan
Spikenard
Corvalol
Notes
References
External links
Valerian, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, US National Institutes of Health, October 2020
Kata Kunci Pencarian: valerian herb
valerian herb
Daftar Isi
VALERIAN - Uses, Side Effects, and More - WebMD
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) is an herb native to Europe and parts of Asia. Valerian root has a long history of use as a sedative. Valerian can grow to be just over 6 feet tall and...
Valerian (herb) - Wikipedia
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis, Caprifoliaceae) is a perennial flowering plant native to Eurasia. It produces a catnip -like response in cats.
Valerian: A safe and effective herbal sleep aid? - Mayo Clinic
Feb 15, 2018 · Results from multiple studies indicate that valerian — a tall, flowering grassland plant — may reduce the amount of time it takes to fall asleep and help you sleep better. Of the many valerian species, only the carefully processed …
How Valerian Root Helps You Relax and Sleep Better - Healthline
Aug 29, 2023 · Valerian is an herb that’s commonly used as an ingredient in sleep aid supplements. It may also help you relax, as well as help reduce mood symptoms like anxiety.
Valerian - Health Professional Fact Sheet - Office of Dietary ...
Valerian is an herb sold as a dietary supplement in the United States. Valerian is a common ingredient in products promoted as mild sedatives and sleep aids for nervous tension and insomnia. Evidence from clinical studies of the efficacy of valerian in treating sleep disorders such as insomnia is inconclusive.
Valerian Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com
Sep 30, 2024 · Valerian is a flowering plant, the root of which is dried and used as an herbal remedy. Valerian has been used in alternative medicine as a possibly effective aid in treating sleep problems (insomnia).
Valerian Root Benefits, Uses, Dosage and Side Effects - Dr. Axe
Sep 23, 2023 · This natural and herbal sleep aid is called valerian root. A systematic review and meta-analysis including 16 evidence-based studies indicates that valerian root is widely used and respected by the general population and physicians for its …
Valerian (Root): Uses, Benefits, Side-Effects - Holland & Barrett
Jun 1, 2021 · Find out all about valerian, including what it does, the benefits to taking it and how much you might need. What is valerian? Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) is a herb that’s renowned for its calming, sedative effects.
Valerian Root: 5 Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, and More - Health
Jan 15, 2025 · Valerian root is an herbal supplement that can improve sleep and ease tension headaches. It’s also been shown to reduce anxiety and depression.
Valerian (Valeriana officinalis): Health Benefits, Ayurvedic Uses
Feb 15, 2025 · The root extract of valerian herb aids memory improvement by potentially lowering stress and anxiety through its interaction with the GABA neurotransmitter in the brain. The herb’s valerinic acid promotes problem-solving abilities and memory performance in both adolescents and children. Ayurvedic Properties Of Valeriana. Rasa (taste): Katu ...